Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is one of the most common sexual health concerns in men, affecting millions worldwide. While it can be caused by a range of physical and psychological factors, modern medicine has developed highly effective treatments to help men regain sexual confidence and performance.
One of the most widely prescribed classes of ED drugs is PDE5 inhibitors — medications like Vilitra (Vardenafil), Viagra (Sildenafil), and Cialis (Tadalafil).
This guide explains how these medications work, why they’re effective, and what you should know before using them.
Understanding the Basics of an Erection
- Before learning how ED medications work, it’s important to understand what happens in the body during an erection:
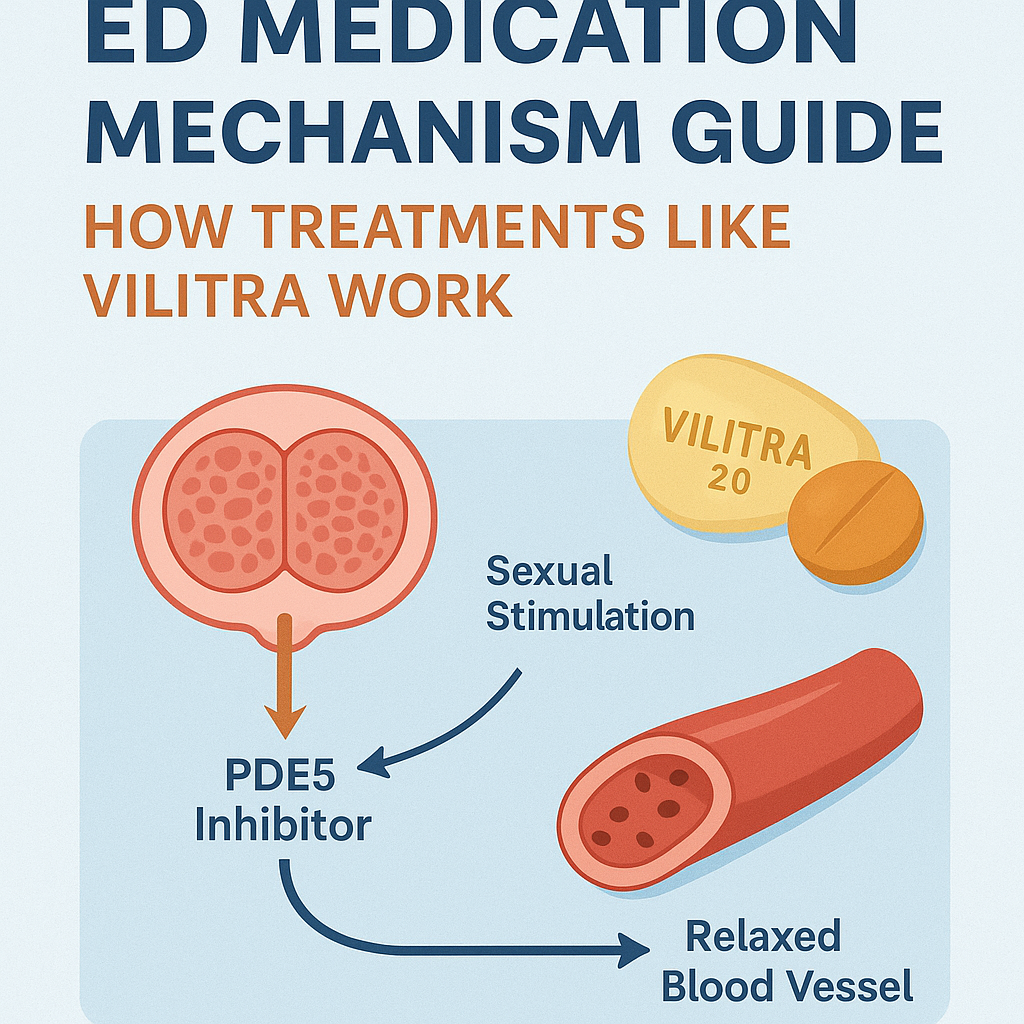
- Sexual Stimulation → triggers the brain to send signals to the penile nerves.
- Nitric Oxide Release → nerves release nitric oxide (NO), which relaxes smooth muscles in the penile blood vessels.
- Increased Blood Flow → relaxed vessels allow more blood to flow into the penis.
- Trapping the Blood → tissues swell, trapping blood and maintaining an erection.
- When there’s a problem in this chain — whether due to poor blood flow, nerve damage, or other health issues — erectile dysfunction occurs.
The Role of PDE5 in Erectile Dysfunction
Inside the penile tissue, a chemical called cGMP is responsible for relaxing blood vessel muscles so blood can enter.
An enzyme called phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) breaks down cGMP.
In men with ED, PDE5 can be overactive, breaking down cGMP too quickly — which means erections are weaker or don’t last long enough.
How PDE5 Inhibitors Work
PDE5 inhibitors like Vilitra (Vardenafil), Sildenafil (Viagra), and Tadalafil (Cialis) block the PDE5 enzyme.
This allows cGMP to remain active for longer, keeping the blood vessels relaxed and the penis engorged during sexual stimulation.
Key points:
- They don’t cause erections automatically — sexual arousal is still necessary.
- They enhance natural processes — improving the body’s own ability to respond to arousal.
- They work temporarily — effects last from 4 hours (Vardenafil) to up to 36 hours (Tadalafil).
Differences Between Common PDE5 Inhibitors
| Medication | Active Ingredient | Onset Time | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vilitra 20 MG | Vardenafil | 30–60 min | ~5 hours |
| Viagra | Sildenafil | 30–60 min | ~4–6 hours |
| Cialis | Tadalafil | 30 min | Up to 36 hours |
Factors That Affect ED Medication Effectiveness
Food intake → High-fat meals can delay absorption for some drugs like Vilitra and Viagra.
Alcohol use → Can reduce effectiveness and increase side effects.
Underlying health conditions → Heart disease, diabetes, and hormonal imbalances can influence results.
Drug interactions → Nitrates and certain blood pressure medications can cause dangerous drops in blood pressure when combined with PDE5 inhibitors.
Potential Side Effects
While generally safe, ED medications can cause:
- Headache
- Flushing
- Nasal congestion
- Indigestion
- Dizziness
Rare but serious side effects include priapism (prolonged erection), sudden hearing loss, or vision changes — requiring immediate medical attention.
Who Should Not Take PDE5 Inhibitors
- Men using nitrates or nitric oxide donors.
- Those with severe heart or liver disease.
- Anyone advised against sexual activity by a doctor.
Conclusion
PDE5 inhibitors like Vilitra 20 mg are highly effective for many men with ED, working by enhancing natural blood flow mechanisms in the penis. Understanding how they work not only helps you make informed choices but also ensures safer and more effective use.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting treatment, as ED can be a sign of underlying health issues.
Related Reading:
Vilitra 20 mg – Uses, Dosage, and Side Effects
Vilitra vs. Viagra – Which One Should You Choose?
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before use.